As concerns over water scarcity and conservation grow across the United States, the practice of rainwater harvesting is gaining momentum as a sustainable solution. A rainwater collection system allows homeowners and businesses to capture and store this valuable resource, including rainy water, reducing their reliance on municipal water supplies and promoting environmental stewardship.
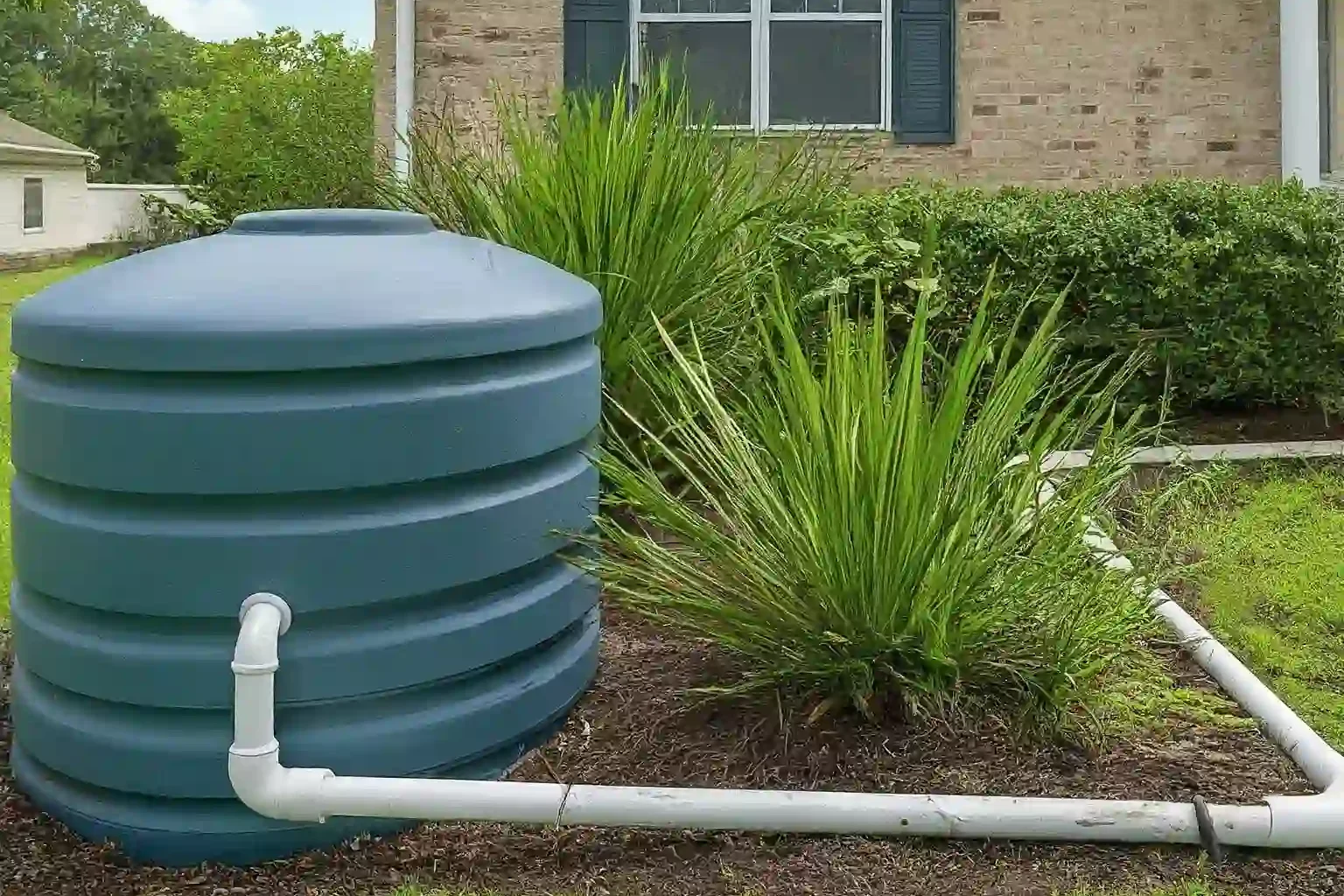

Table of Contents
Environmental Benefits of Collecting Rainwater
Implementing a rain water collection system offers numerous environmental benefits for US households and communities:
- Water Conservation
- Reduced Runoff and Erosion
- Lower Energy Consumption
- Groundwater Recharge
How to Set Up Your Own Rainwater Collection System
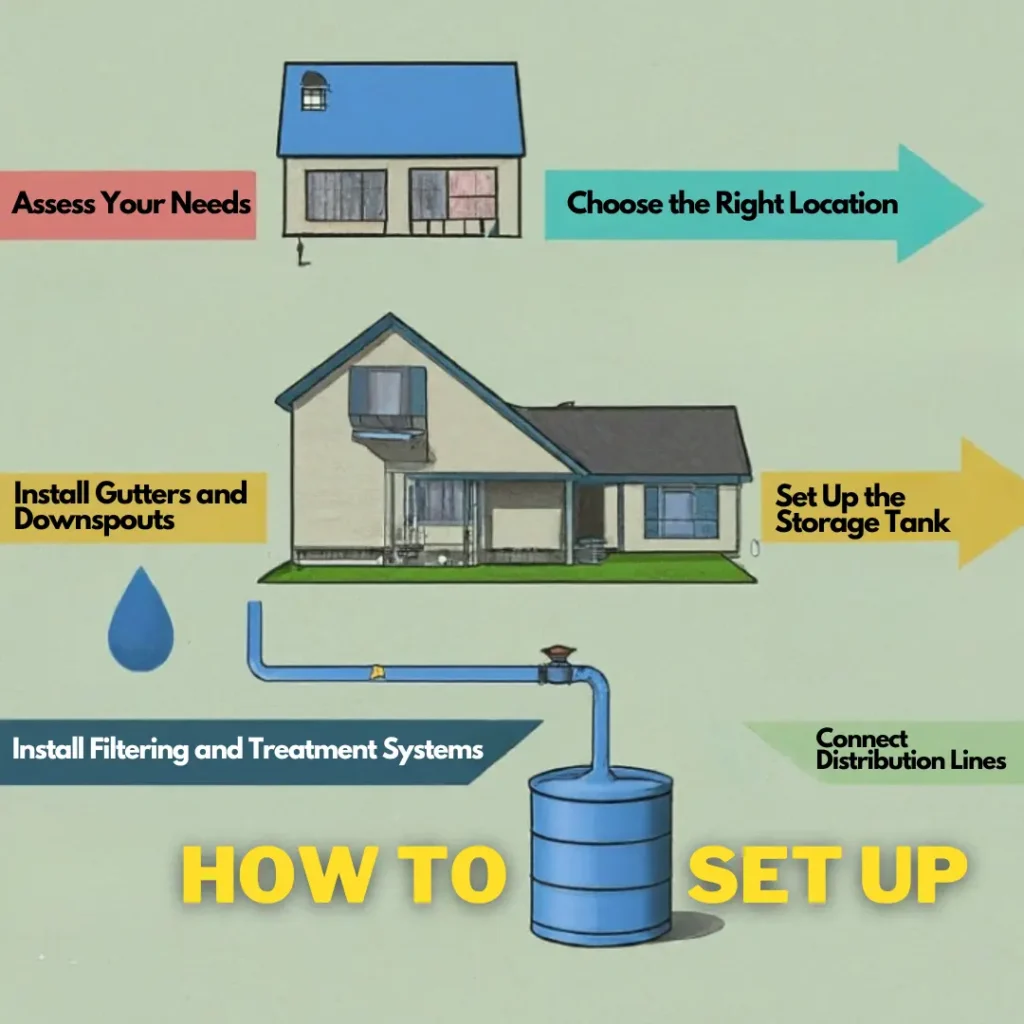
Setting up a rainwater collection system in the US may seem daunting, but with careful planning and execution, it can be a rewarding and cost-effective endeavor. Follow these general steps:
- Assess Your Needs: Determine your water usage requirements and the available roof area for capturing rainwater. This will help you size your water catching system appropriately.
- Choose the Right Location: Identify a suitable location for your rainwater harvesting tank, considering factors such as accessibility, proximity to the intended usage areas, and local building codes.
- Install Gutters and Downspouts: Ensure that your roof has functional gutters and downspouts to channel rainwater effectively into the collection system.
- Set Up the Storage Tank: Select an appropriate storage tank size based on your needs and available space. Common options include plastic, fiberglass, or concrete rainwater collection tanks.
- Install Filtering and Treatment Systems: Incorporate filtering mechanisms, such as leaf screens and sediment filters, to remove debris and contaminants from the collected rainwater. Depending on your intended use, additional treatment systems may be required.
- Connect Distribution Lines: Install piping and distribution lines to transfer the collected rainwater from the storage tank to the desired usage points, such as irrigation systems or plumbing fixtures.
Components of a Rainwater Collection
A typical rainwater collection system comprises several key components:
- Catchment Area: This is the surface area, usually a roof, where rainwater is collected.
- Gutters and Downspouts: These channels direct the collected rainwater from the catchment area to the storage tank.
- Leaf Screens and Filters: These devices prevent debris, leaves, and other contaminants from entering the storage tank, ensuring the collected water remains clean.
- Storage Tank: The central component of the system, the storage tank holds the collected rainwater until it is needed for use.
- Overflow Pipes: These pipes divert excess water away from the storage tank during heavy rainfall, preventing overflow and potential damage.
- Distribution System: This includes pumps, piping, and fixtures that transport the collected rainwater to its intended usage points, such as irrigation systems or plumbing fixtures.
How to Maintain Your Rainwater Collection System
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and efficiency of your rainwater collection system. Here are some essential maintenance tasks:
- Clean Gutters and Downspouts
- Inspect and Replace Filters
- Monitor Water Quality
- Maintain Storage Tank
- Winterize the System
Legal Considerations and Regulations
Before installing a rainwater collection system in the US, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with local and state regulations governing rainwater harvesting. Some states, like Colorado, Texas, and Virginia, have specific laws and guidelines in place, while others may have minimal or no regulations. Consulting with local authorities and adhering to relevant codes and guidelines is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
Maximizing Water Usage with Rainwater
To fully leverage the benefits of your rainwater collection system, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Integrate with Irrigation Systems: Connect your rainwater storage tank to your landscaping irrigation system, enabling you to use collected rainwater for watering gardens, lawns, and outdoor plants, reducing your reliance on municipal water sources.
- Use for Non-Potable Purposes: Utilize collected rainwater for non-drinking purposes, such as flushing toilets, washing cars, or cleaning outdoor surfaces, further reducing your municipal water consumption.
- Rainwater Harvesting for Potable Use: In some states like Texas and Arizona, collected rainwater can be used for drinking and cooking purposes with proper treatment systems, maximizing the system’s potential.
- Rain Barrel Water Systems: Consider installing a rain barrel water system to collect and store smaller amounts of rainwater for specific purposes, such as watering potted plants or washing vehicles.
Case Studies
Numerous successful rainwater collection projects have been implemented across the United States, demonstrating the practicality and effectiveness of these systems. Here are a few notable examples:
- The Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center in Austin, Texas: This renowned botanical garden has an extensive rain water collection system, capturing water from roofs and hardscapes, and using it for irrigation and other non-potable purposes.
- Rainwater Harvesting in Tucson, Arizona: The city of Tucson has actively promoted rainwater harvesting through rebate programs and educational campaigns, encouraging residents to install systems and conserve water in this arid region.
- The Sidwell Friends School in Washington, D.C.: This prestigious school has implemented a comprehensive rainwater harvesting system, collecting water from rooftops and using it for toilet flushing and irrigation, reducing the school’s water consumption by over 2 million gallons annually.
Innovations and Trends
As the demand for sustainable water management solutions grows in the US, rainwater collection systems are continuously evolving. Some exciting innovations and trends in this field include:
- Smart Monitoring and Control Systems: The integration of smart sensors, IoT (Internet of Things) technologies, and remote monitoring capabilities allows for real-time monitoring and optimization of rainwater collection systems, enhancing efficiency and water usage.
- Advanced Water Treatment Technologies: Emerging water treatment technologies, such as membrane filtration and ultraviolet disinfection, enable the safe and reliable use of collected rainwater for potable purposes, expanding the potential applications of rainwater harvesting.
- Integration with Green Building Practices: Rainwater collection systems are increasingly being incorporated into green building designs and sustainable community development projects across the US, contributing to overall environmental sustainability and water resilience.
- Community-Scale Rainwater Harvesting: Beyond individual household systems, larger-scale community rainwater harvesting projects are gaining traction in the US, offering centralized water catchment and distribution networks for entire neighborhoods or districts.
Summary
As water scarcity concerns grow in various regions of the United States, embracing rainwater collection systems becomes an increasingly crucial step toward a more sustainable future. By capturing and utilizing this valuable resource, US households and communities can reduce their reliance on strained municipal water supplies, mitigate environmental impacts, and promote water conservation.
Rainwater harvesting not only contributes to environmental sustainability but also offers potential economic benefits through reduced water bills and long-term cost savings. By adopting this practice, US residents and businesses can play an active role in preserving our precious water resources for future generations.
Embrace the concept of rain water collection today and join the growing movement toward sustainable water management practices in the United States. Every drop of rainwater collected and reused is a step closer to a more water-secure and environmentally conscious future for our nation.




